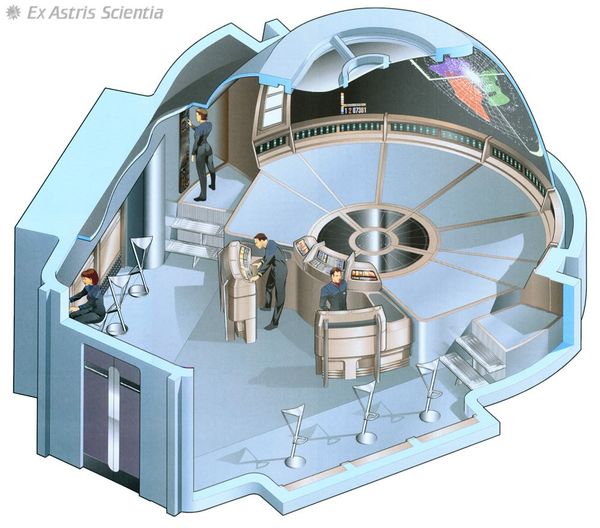
The subspace accelerator is an experimental device construction by Section 31 to experiment with propelling a warp capable vessel at many times its normal maximum velocity. The construction was based on a stellar observatory design, it contains only one main room with a transporter room attached and service crawl-ways to access systems for maintenance. The stations bridge / control room is based on the USS Voyager Stellar Cartography design, the large holographic display ideal of experiments of speed acceleration.
Operation
The central dish is used to project the subspace field over a test area. Subspace energy is funneled from nearby distortions using the three arms of the station which can be directed to point toward a specific anomaly or energy source. The structure funnels this energy into the main dish with uses it to project the subspace acceleration field at an object or area.
Theory
In theory, when the energy builds to sufficient power a graviton pulse from the station interacts with a vessels warp field and drive coils to propel it at high but controlled velocities. In actuality the field reacted in an unstable way with the warp fields within the target area during a reactor test. A feedback loop along the stations accumulators and the projection dish occurred and the computer attempted to discharge the energy through the dish into the test field. This discharge pushed the field out of normal space to previously unheard of velocities.
It is unknown if the inside of the field would remain stable and thus survivable by any ships within the field.