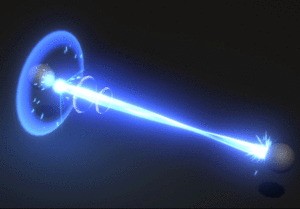
The repair beam is a highly advanced mix of technologies used to repair damaged systems and materials at a highly accelerated rate. It blends a type of molecular quasi-matter with molecular replicators / transporter technologies. The system is designed to project material onto a remote location within a maximum of 2 meters in layers at a molecular scale. In this way it projects material onto a damaged or empty space and binds this matter to existing matter at the target location constructing new material from a molecular level. In this way it is able to effect repairs are an incredibly high rate of speed.
Process
Usually used in tandem, one repair beam will be used in a recycling phase feeding an atomic matter stream from damaged materials into the pattern buffer. The other beam will then pull the atomic matter stream patterned at a molecular level to reconstruct damaged components. The repair beams can operate at around 161 cubic centimeters of matter per second on average. Specific rates will depend on the repair being done and the environment.
Repair Phase
- . The recycled based-atomic matter stream is resequenced into molecular matter for use by micro-replicators.
- . Micro-replicators operating with molecular resolution which produce microscopic amounts of matter very quickly, on the level of 150 cubic micrometers.
- . Replicated matter is partially dematerialized and phased by a molecular level micro-transporter node generating an equal mass quantity of quasi-matter.
- . Quasi-matter is transmitted along a focused phased plasma beam path to the target surface, where it collects in a phased state between matter an energy.
- . Collected quasi-matter is de-phased and materialized in its original pattern by the molecular level micro-transporter node.
Recycling Phase
- . A micro-transporter node operating in molecular resolution dematerializes unwanted, damaged, or otherwise unusable waste-matter./
- . Recycled matter is stored within a transporter pattern buffer and is molecularly resequenced into base materials at the atomic level.
Power Usage
The repair beam is a very energy-intensive endeavor, relying on being able to recycle existing matter in the form of dematerializing damaged materials. Even with this recycling of waste materials it is a power-intensive process, which does not replace conventional repairs.